Password security
Good passwords are one of the most important countermeasures against data leakage. We will discuss what constitutes a good password below.
- passwords secure encrypted data, such as: hard drives and password databases
- passwords secure access to online accounts: against non-authorities!
- authorities like the police, might be able to get a court order, because your data is stored there unencrypted, so they don’t need your password.
That’s why it’s our duty as modern activists to use a password manager. It helps us meet all these requirements without much difficulty. This way, we not only protect our own access, but also the information behind it that is linked to our comrades!
In this article you will find explanations on:
- What a password manager is capable of
- What a good password is
- What second factor authentication means and why it is recommended
Password managers
A password manager stores all your passwords in a single encrypted database (which is just a file) protected by a master password. This means that your passwords are not stored in plain text on your system or on paper in your home, and you don’t have to remember them all yourself.
Since you no longer have to remember passwords yourself, it is not a problem and is also recommended that you generate a separate, strong password for each account. This is very easy to do with the password manager itself.
The password manager also stores the assignment to websites & apps for which you have generated the respective password. This also makes phishing more difficult, because the password will not be displayed as a suggestion on a false URL.
As mentioned above, the password manager itself is protected by a strong master password and/or other factors (see below 2-factor authentication). This is therefore (apart from hard drive encryption) the only password you really need to remember and can therefore be a little more complex. The rule is: it is better to remember one strong password than many insecure passwords.
Read more about this in the recommendations for password managers.
Strong passwords
Okay, but you still need at least one strong password for the password manager. But when is a password strong?
An important basic requirement is that the password is generated randomly. Anything you come up with, no matter how clever your system may be, should be considered insecure.
Optimized algorithms enable authorities to search specifically for possible passwords used by activists by trying out vocabulary, quotes from revolutionary writings and songs, etc., while saving time and energy by avoiding fascist vocabulary, for example.
“History is a history of class struggles” may have seven words, but for the reasons mentioned above, it is a very poor password!
Here you can already see that the term passwords also refers to passphrases. Passphrases are randomly generated strings of words. They have the advantage that people can remember much longer strings of characters.
- At least 5 words long, preferably 7
- Created using a password manager or Diceware (dice and a list).
We explain below where the numbers 5 and 7 come from. There, we look at how long it would theoretically take to crack a randomly generated password or passphrase. However, these tables are always subject to many ifs and buts.
2-factor authentication
2FA ensures that simply entering a password is not sufficient for complete authorization, as it is assumed that passwords may be corrupted. Therefore, a second instance is requested for complete authorization.
The recommendations for password managers include an example scenario showing how a KeePassXC database can be secured with a second factor.
The second factor can be based on various characteristics:
2nd factor: Possession
You need a special device that either displays a number or must be plugged into the computer via USB. If the attacker does not have this “device,” authorization will not be granted. (Hardware tokens, 2FA apps, SMS)
TOTP software
TOTP stands for time-based one-time password and can be set up with all common password managers such as KeePassXC. The login process then consists of entering your username and password, after which you will be asked for the TOTP (e.g., a 6-digit PIN), which changes every ~30 seconds.
USB hardware tokens
These look like normal USB sticks. If a service/hard drive or similar configured with this token is to be unlocked, the stick must also be inserted into the device being used. These tokens are often protected with a PIN, so stealing them is not enough. The number of PIN attempts is limited.
Since all of this is implemented and protected at the hardware level, it is a very secure method of authentication. (The relevant standard for security tokens of this type is called FIDO2, the old standard is U2F.)
TOTP hardware tokens
Similar to TOTP software, but not in an app such as a password manager, but as a thumb-sized device. They have a small screen that displays the 4-6 digit TOTP, which changes every ~30 seconds.
When logging in, the code displayed at that moment must always be entered as 2FA. However, the standards for tokens of this type are usually not open source, which is why we do not recommend using them.
SMS
Probably the better-known method. To verify the identity of the user, the respective service sends an SMS to the phone number registered with the account. Since the mobile network cannot be considered secure, we do not recommend this method.
2-factor biometrics
Unique biometric characteristics must be verified during registration (fingerprint, facial recognition, iris scan). Biometric authentication is particularly widespread for smartphones.
However, biometric authentication poses a problem for us in that the authorities can simply use our biometric characteristics under duress and by force. We therefore advise against biometric unlocking methods such as fingerprint and Face ID as a matter of principle.
Technische Details
Technische Details
Biometrics such as fingerprints or facial recognition have been proven to be falsifiable. Starbug from the CCC has already demonstrated how easy this is for fingerprints, faces, iris and vein recognition. The most important point here, however, is that you can never change your biometric characteristics. A corrupted password can be reset. A fingerprint or face, however, cannot.
The only exception to this is GrapheneOS, which offers a PIN as a second factor limited to twenty attempts for fingerprint recognition and otherwise meets the highest security standards.
2nd factor: Knowledge
For example, the security questions that were common in the past, such as “What is your place of birth?” However, these “security questions” usually imply answers that someone who knows you well could easily find out for themselves. We therefore don’t recommend them.
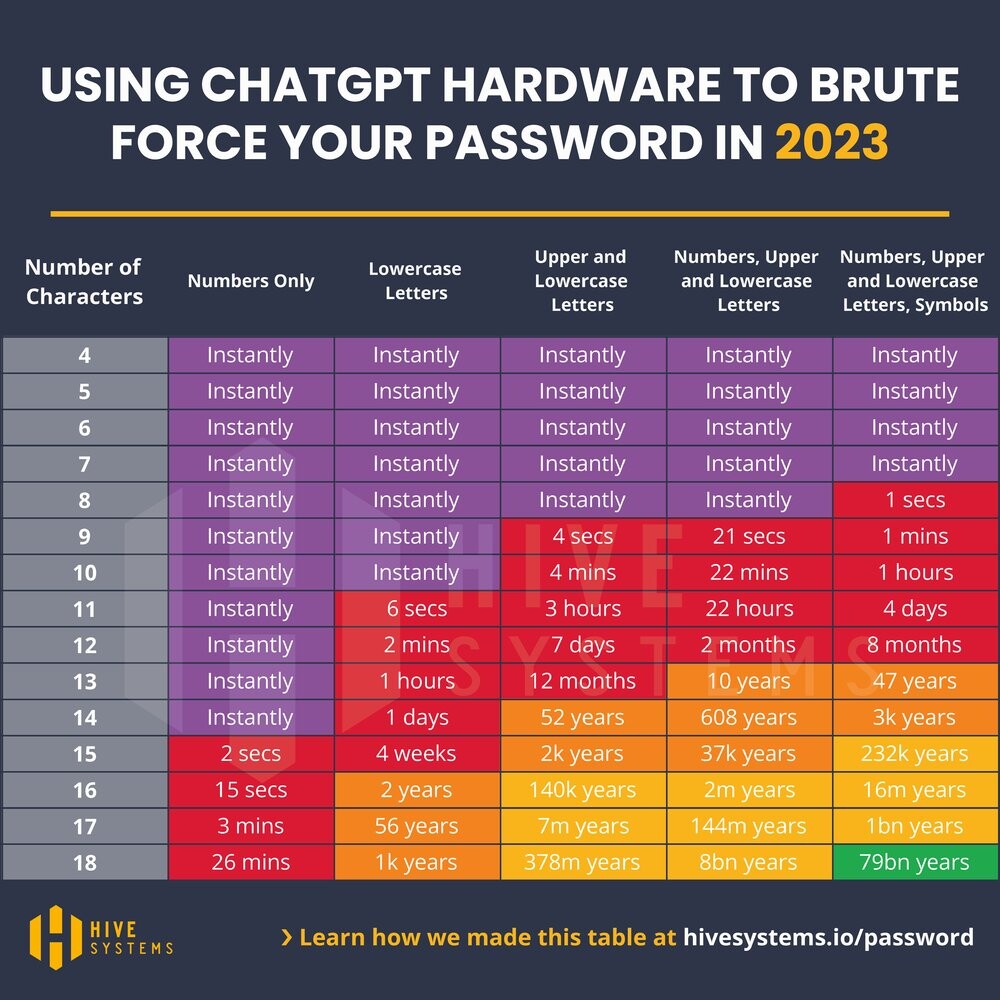
Time to crack
In reality, how long it takes to crack a password depends very much on the exact circumstances. The calculations here assume a very specific scenario. The scenario shown here assumes very favorable conditions for the attackers. This means that in practice, it will take even longer.
Time to crack a password
It should also be noted that these times are for one password from one person. All of the hardware is busy with this task, so no other passwords can be cracked during this time.
Technische Details
Technische Details
We assume an MD5-hashed password and that the attackers have access to the hardware used to train ChatGPT: 10,000 NVIDIA A100 GPUs. Purchase price: approx. $9,000 per unit (2024) for the cheaper version with 40GB of memory. That’s a total of $90 million. Even renting this amount of hardware is not cheaper in the long run. Further details on the scenario can be found at hive-systems, who performed the calculations.
Important prerequisite: The password must have been generated randomly! This means that this is purely character brute forcing. So, for example, you start with 0000 and try:
0001,0002,...,AAAA,AAAB,...,A-A-A-B-B,R€70lut10n,- …
etc. without word lists optimized for the target person.
Time to crack a passphrase
However, a random password that is sufficiently long and contains letters, numbers, and special characters is difficult for humans to remember. That’s why we recommend using passphrases for passwords that you need to remember, such as those for your password manager and the hard drive of your computer and phone. These consist of words instead of individual letters. They are much easier for humans to remember, but are no less secure than passwords. See also: xkcd 936
Technische Details
Technische Details
In information theory, it must always be assumed that the attacker knows how we created the password in order to evaluate its security. Therefore, the attacker uses a word list attack here. Otherwise, everything remains the same.
For example, the word case is assumed below, namely that the attackers know exactly how many words from which language and in which format (i.e., upper/lower case, which characters between words) were used for the password and that they use (in the left column) the hardware used to train ChatGPT to crack it. Therefore, these graphics should not be taken at face value.
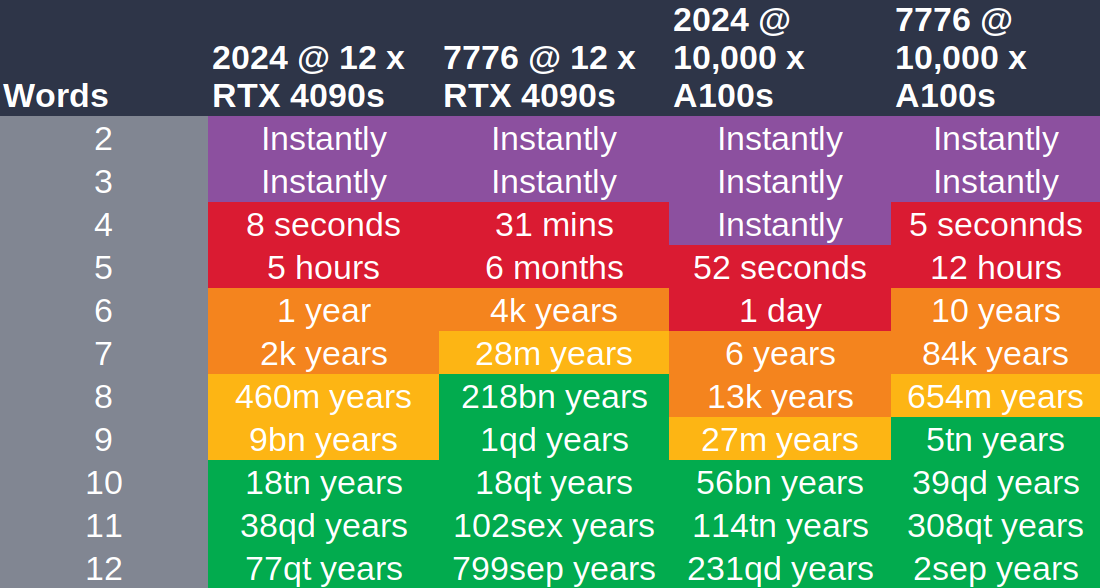
As already mentioned, random passphrases can be created using password managers or, in a similar way, with dice and a word list that is as large as possible.
Feedback: You have feedback for esc-it.org? Feel free to use our short feedback form.